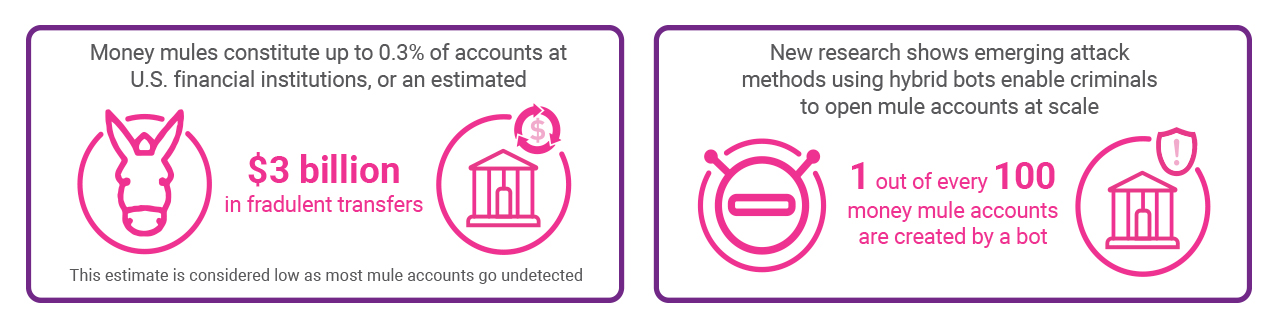
Money mule fraud is a type of financial scam in which criminals exploit individuals, known as money mules, to transfer stolen money or the proceeds of illegal activities.
Money mule accounts are becoming increasingly difficult to distinguish from legitimate customers, especially as criminals find new ways to develop hard-to-detect synthetic identities.
How money mule fraud typically works:
Recruitment: Fraudsters seek out potential money mules through various means, such as online job ads, social media, or email/messaging apps.
They will often pose as legitimate employers offering job opportunities promising compensation or claiming to represent charitable organizations.
Deception: Once a potential money mule is identified, the fraudsters use persuasive tactics to gain their trust. They may provide seemingly legitimate explanations like claiming the money is for investment purposes, charity donations or for facilitating business transactions.
Money Transfer: The mule is instructed to receive funds to their bank or other financial account. The funds are typically transferred from other compromised bank accounts obtained through phishing or hacking. The mule is then instructed to transfer the money to another account, sometimes located overseas.
Layering: To mask the origin of funds and make them difficult to trace, fraudsters will employ layering techniques. They may ask the mule to split funds into smaller amounts, make multiple transfers to different accounts, or use various financial platforms such as money services or crypto.
Compensation: The money mule is often promised a percentage of transferred funds as payment. However, the promised monies are lower than the dollars transferred, or sometimes the mule receives no payment at all.
Legal consequences: Regardless whether mules know they are supporting a criminal enterprise or are unaware, they can face criminal charges. In addition, their personal information could be compromised leading to identity theft and financial loss.
How can banks get ahead of the money mule curve:
- Know your beneficiaries
- Monitor inbound payments
- Engage identity verification solutions
- Create a “Mule Persona” behavior profile
- Beware that fraudsters will coach the mule, therefore confirmation of payee is no longer a detection solution
- Educate your customers to be wary of job offers that seem too good to be true and remain vigilant of requests to receive and transfer money, particularly from unknown individuals and organizations.
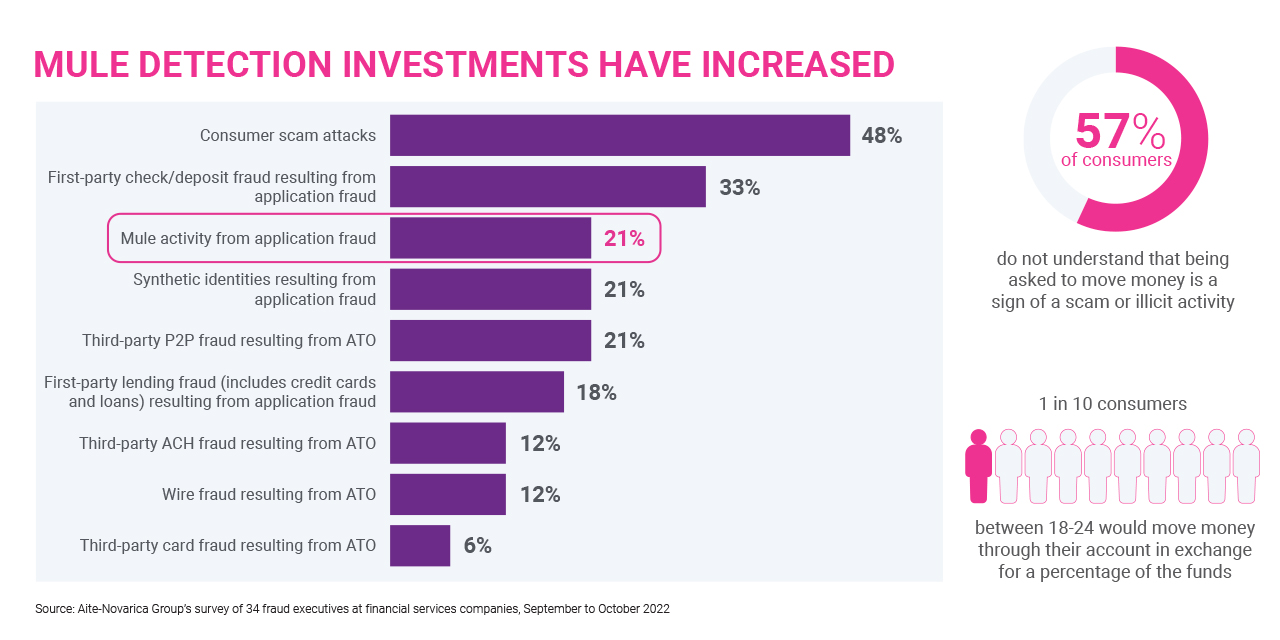
How financial institutions can mitigate money mule fraud risk
When new accounts are opened, a financial institution usually doesn’t have enough information to establish patterns of behavior with newly registered users and devices the way they can with existing users. However, an anti-fraud system should catch a known behavior profile that has been previously identified as malicious. In this situation, the best practice is to compare the new account holder’s behavior against a representative pool of customers, which will analyze things like:
- Spending behavior compared to the average
- Payee profile
- Sequence of actions
- Navigation data related to machine-like or bot behavior
- Abnormal or risky locations
- The account owner’s relations to other users
The risk engine needs to be able to collect and score data across all digital channels to allow the financial institution to detect all possible relationships to users, IP addresses and devices that have proven fraud behavior. This includes information about the user, account, location, device, session and payee, among others. If the system notices any unusual changes in the account holder’s personal information, the decision engine will flag it for review. It can then be actively monitored and investigated, if necessary.
The benefits of machine learning
This is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can analyze vast amounts of disparate data across digital channels in real time. Anti-fraud systems based on AI analytics and predictive analytics models have the ability to aggregate and analyze data on multiple levels. This allows a financial institution to instantly detect all possible relationships across users, devices, transactions and channels to more accurately identify fraudulent activity.
When suspicious behavior is flagged via a high risk score, the risk engine can then drive a dynamic workflow change to step up security or drive a manual review process. It can then be actively monitored by the fraud prevention team and escalated for investigation.
How Experian can help
Experian’s fraud prevention solutions incorporate technology, identity-authentication tools and the combination of machine learning analytics with Experian’s proprietary and partner data to return optimal decisions to protect your customers and your business.
To learn more about how Experian can help you leverage fraud prevention solutions, visit us online or request a call


